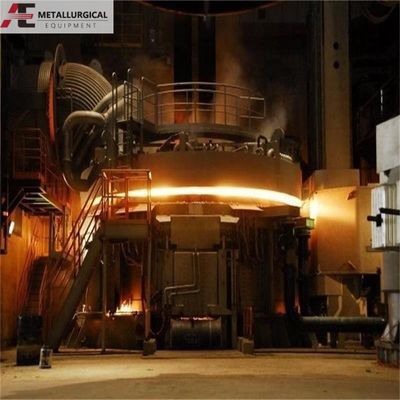
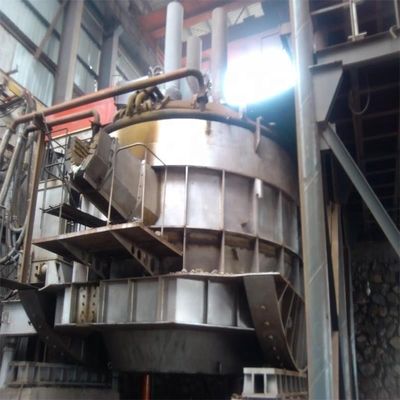
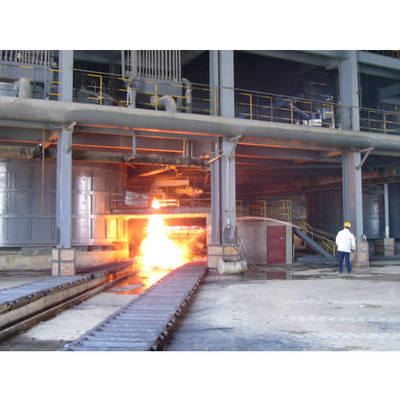
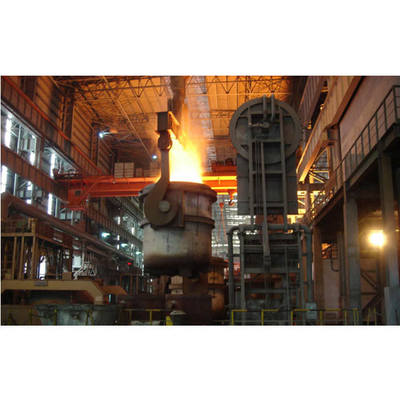
Fabricação de aço por forno de arco elétrico: principais etapas do processo e tendências de desenvolvimento
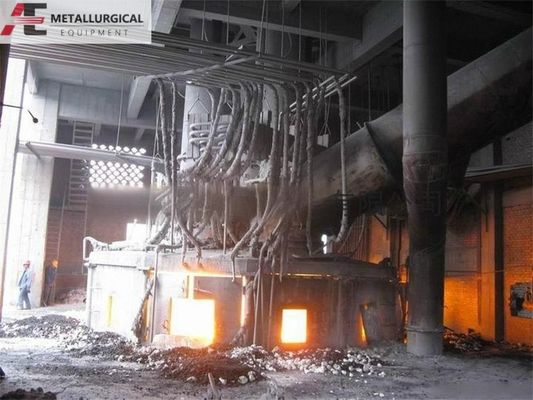
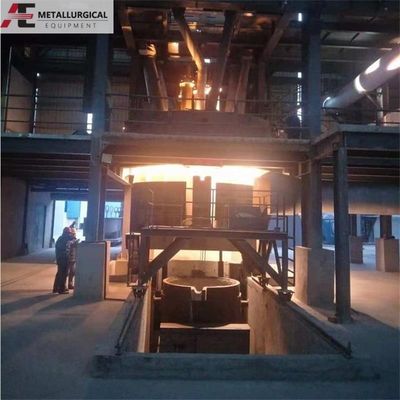
Fornos de arco elétrico(EAF) A siderurgia é um método primário para a produção de aços de liga média e alta e de graus especiais de alta qualidade.Os FEA também são cada vez mais utilizados para fabricar aços de carbono comuns., ganhando progressivamente parte do mercado a nível mundial.
Com o progresso industrial e tecnológico em curso, a procura de ligas e aços premium continua a crescer.O aço para fornos eléctricos já representava cerca de 30% da produção mundial total de aço bruto..
Visão geral do processo
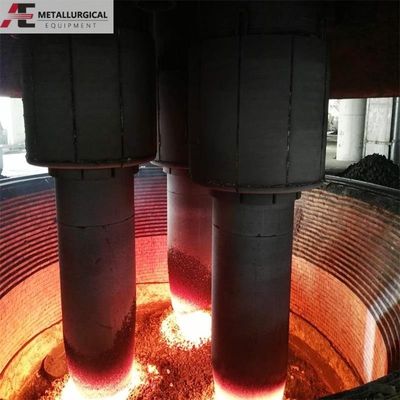
A siderurgia EAF depende predominantemente do aquecimento por arco, com temperaturas de zona de arco que atingem até 4000°C. O ciclo de fusão é tipicamente dividido em três fases: fusão, oxidação e redução.O ambiente do forno pode ser controlado para criar condições de oxidação ou redução, permitindo uma desfosforização e uma dessulfuração de elevada eficiência.
Características essenciais da siderurgia da EAF
A utilização de sucata de aço como principal matéria-prima reduz o investimento de capital em comparação com as rotas integradas.O desenvolvimento de processos de redução directa permitiu a utilização de grânulos metalizados (DRI/HBI) para substituir uma parte significativa da sucata, reforçando ainda mais o papel dos FEA na siderurgia moderna.
No mundo, existem cerca de 1.400 FEA de grande escala em operação. As tendências actuais apontam para o aumento do tamanho dos fornos, projetos de ultra-alta potência e a adopção generalizada do controlo de processos informatizado,com os maiores fornos de capacidade superior a 400 t.
Padrões globais e regionais
A nível internacional, a maior parte dos fornos eléctricos de mais de 150 t são utilizados para a produção de aços comuns, sendo que os aços de baixo carbono representam 6080% da produção de fornos eléctricos em muitos países.No entanto, onde o abastecimento de energia e a disponibilidade de sucata têm sido historicamente limitações, os EAF são utilizados principalmente para a produção de aço de alta qualidade e liga.
Características do produto
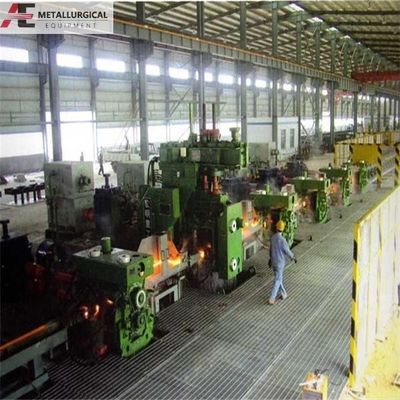
O aço produzido pela EAF refere-se tipicamente às qualidades fundidas em fornos de arco com revestimento básico.que apresentam uma excelente uniformidade, propriedades mecânicas superiores e melhor equilíbrio resistência-ductilidade em níveis de carbono dados em comparação com os aços convencionais de fogão aberto.
Flexibilidade das matérias-primas
Embora o sucata permaneça o material de carga dominante, os FEA podem também utilizar ferro esponja (DRI) para substituir parcialmente o sucata,e certas poeiras/lodos metalúrgicos podem ser incorporados através de tecnologias de reciclagem adequadasOs aditivos de liga são feitos para ajustar com precisão a composição química e atender às faixas de teor especificadas para os elementos de liga.
Em resumo, a siderurgia EAF continua a evoluir em direcção a uma escala maior, a uma maior eficiência energética, a uma maior automação e a uma maior versatilidade das matérias-primas.posicioná-lo como uma tecnologia central para a produção de aço, tanto orientada para a qualidade como para a eficiência dos recursos.
Somos um fabricante profissional de fornos elétricos. ou se você precisar de fornos de arco submerso, fornos de arco elétrico, fornos de refinação, ou outros equipamentos de fusão,Por favor, não hesite em contactar-nos emSusana@aeaxa.com

 Por favor verifique seu email!
Por favor verifique seu email! Por favor verifique seu email!
Por favor verifique seu email!  Por favor verifique seu email!
Por favor verifique seu email! Por favor verifique seu email!
Por favor verifique seu email! 








